Building a Lexical Analyzer and SLR Parser in Java

Introduction
In the realm of compiler design, two crucial components stand out: the Lexical Analyzer and the Parser. This project dives deep into implementing both, using Java as our weapon of choice. Let’s embark on this journey of transforming raw code into meaningful structures!
Part 1: The Lexical Analyzer
What is a Lexical Analyzer?
A lexical analyzer, often called a scanner or tokenizer, is the first phase of a compiler. It takes the raw input code and breaks it down into a sequence of tokens. Think of it as the first pass in understanding the structure of the code.
Our Implementation
Our lexical analyzer is implemented in Java and can recognize a wide variety of tokens, including:
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Literals (integer, floating-point, character, string)
- Operators
- Punctuation
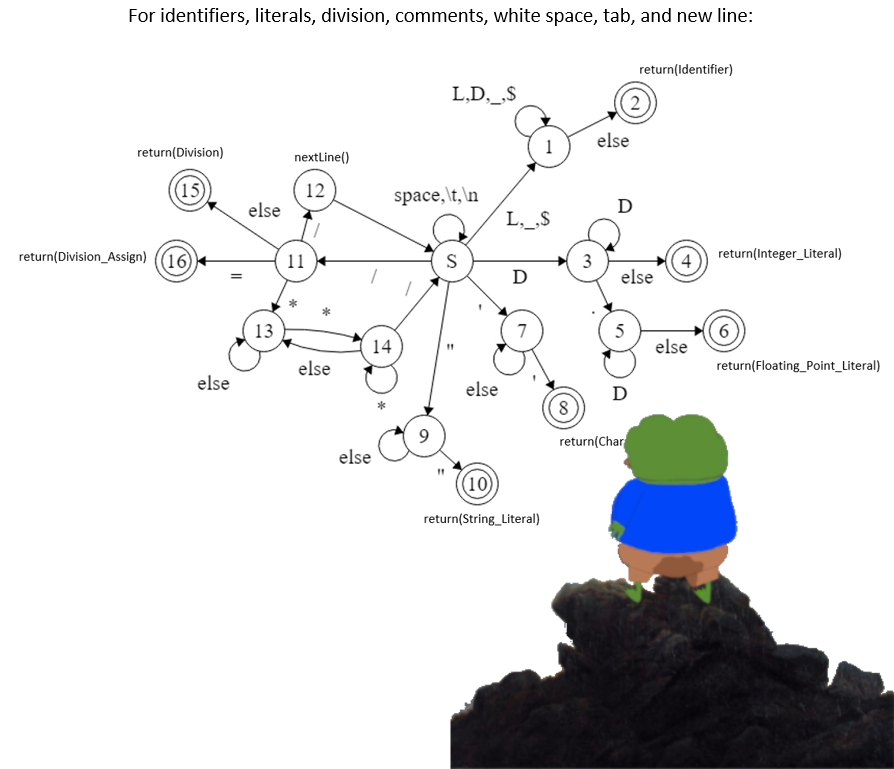
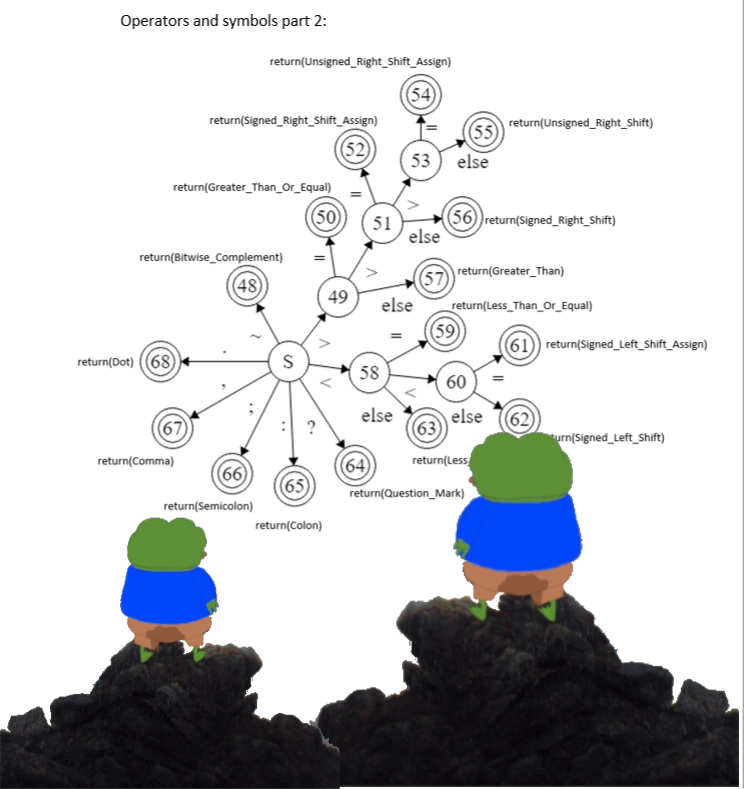

Implemenation Details
Here is the detailed implementaion of the lexical analyzer. Credits goes to my colleague Khalid AL-Ghamdi <3.
package javalexicalanalyzer;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JavaLexicalAnalyzer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException {
tokenizer("input.txt"); //input can be changed from here
System.out.println("Tokens have been identified successfully !!!");
System.exit(0);
}
public static void tokenizer(String location) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException{
if(!(new File(location).exists())){
System.out.println("The Input File Does Not Exist");
return;
}
char lexeme []= new char[30]; //to store lexeme to turn into token later
int index=0; //the index of the char in the lexeme
String currentLexeme; // to print the lexeme as a string later
boolean keywordFlag=false; // true if identifier is a keyword
char lookahead; //the character we are currently reading
String keywords[]=new String [50]; //an array for keywords. note: we have 50 keywords registered in a file
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(location)); //we will use BufferedReader to read char by char from the input file
Scanner keywordScanner = new Scanner(new File("keywords.txt")); // we will use Scanner to read word by word from keywords file to store them in an array
PrintWriter output = new PrintWriter("output.txt");
int k=0;
while(keywordScanner.hasNext()){ //storing keywords in an array
keywords[k]= (String)keywordScanner.next();
k++;
}
int state = 0; //start state (S state in the DFA)
// BufferedReader will read char and return as integer, we need to type cast (char) to turn the integer to char
int charNum; //BufferedReader will return -1 if end of file is reached, which why we need charNum to check
charNum=input.read();
boolean lastRead=false; //without this the lexical analyzer will skip the very last rotation
//because the last rotation will have charNum as -1 but the program didn't yet reach a final state
while(charNum!=-1 || !lastRead){ //while end of file is not reached
if(charNum==-1) // if true it will continue this loop but will exit next rotation
lastRead=true;
lookahead=(char)charNum;
switch(state){
case 0: //start state
if(Character.isWhitespace(lookahead) || lookahead=='\n' || lookahead=='\t'){ //ignore whitespace, new line , and tab
state=0;
charNum=input.read(); // read next character
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='_'|| Character.isLetter(lookahead)|| lookahead=='$'){ //identifier
state=1;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead; //store lookahead in the lexeme array
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(Character.isDigit(lookahead)){ //digit literal (int or floating point)
state=3;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='\''){ //character literal
state=7;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='\"'){ //String literal
state=9;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='/'){ //can be one line comment, multi-line comment, division, or division with assign
state=11;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='+'){ // can be increment, plus , or plus with assign
state=17;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='-'){ // can be decrement, subtract , or subtract with assign
state=21;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='*'){ // multiplication, or multiplication with assign
state=25;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='%'){ // modulus, or modulus with assign
state=28;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='='){ //can be equal or assign
state=31;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='|'){ //can be bitwise, logical , or with assign
state=34;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='&'){ //can be bitwise, logical , or with assign
state=38;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='!'){ // can be logical not or not equal
state=42;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='^'){ // can be bitwise XOR , or XOR with assign
state=45;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='~'){ //bitwise complement
state=48;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead; //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='>'){ //can be greater than, or right shift
state=49;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='<'){ //can be less than, or left shift
state=58;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='?'){
state=64;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead==':'){
state=65;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead==';'){
state=66;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead==','){
state=67;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='.'){
state=68;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='('){
state=69;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead==')'){
state=70;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='['){
state=71;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead==']'){
state=72;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='{'){
state=73;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='}'){
state=74;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='\\'){ //backslash
state=75;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='\b'){ //backspace
state=76;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{ //if a character is read which is not recognized by our tokenizer
state=77;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
case 1:
if(lookahead=='_'|| Character.isLetter(lookahead) || Character.isDigit(lookahead) || lookahead=='$'){
state=1;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else { // identifier is finished
state=2;
lexeme[index]='\0'; //store null (\0) after lexeme so we don't print after null
//charNum=input.read(); <-- we will not use this because we still want to use lookahead since it is not part of the identifier
break;
}
case 2:
state=0;
currentLexeme=""; // now it has nothing and will be filled with the characters of the lexeme in the next loop
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){ // from 0 untill null, null will not be printed
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i]; //add the character to the lexeme string
}
for(int i=0;i<keywords.length;i++){ //to check if identifier is a keyword
if(currentLexeme.equals(keywords[i])){
keywordFlag=true;
index=i; //save i to print the keyword later
break;
}
}
if(keywordFlag){ //lexeme is a reserved word
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,keywords[index]);
keywordFlag=false;
}
else{
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"ID");
}
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 3:
if(Character.isDigit(lookahead)){
state=3;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='.'){ //it is a float point literal
state=5;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else { // integer literal
state=4;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 4:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Integer Literal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 5:
if(Character.isDigit(lookahead)){
state=5;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else {
state=6;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 6:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Floating Point Literal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 7:
if(lookahead=='\''){
state=8;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else {
state=7;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
case 8:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\'',"Single Quote");
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Character Literal");
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\'',"Single Quote");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 9:
if(lookahead=='\"'){
state=10;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else {
state=9;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
case 10:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\"',"Double Quote");
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"String Literal");
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\"',"Double Quote");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 11:
if(lookahead=='/'){ //one line comment
state=12;
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='*'){ // multi-line comment
state=13;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='='){ //division with assign
state=16;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{ //division
state = 15;
lexeme[index]='\0';
index=0;
break;
}
case 12:
state=0;
input.readLine(); //skip the one line comment
charNum=input.read(); //read character from next line
index=0;
break;
case 13:
if(lookahead=='*'){
state=14;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else {
state=13;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
case 14:
if(lookahead=='*'){
state=14;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='/'){
state=0;
index=0;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else {
state=13;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
case 15:
state=0;
// currentLexeme="";
// for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){ <-- no need since we will print only '/'
// currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
// }
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'/',"Division");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 16:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Division Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 17:
if(lookahead=='+'){
state=18;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='='){
state=19;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=20;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 18:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Increment");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 19:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Plus Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 20:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'+',"Plus");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 21:
if(lookahead=='-'){
state=22;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='='){
state=23;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=24;
lexeme[index]='\0'; ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// check if necessary
break;
}
case 22:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Decrement");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 23:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Subtract Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 24:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'-',"Subtract");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 25:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=26;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=27;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 26:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Multiplication Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 27:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'*',"Multiplication");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 28:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=29;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=30;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 29:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Modulus Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 30:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'%',"Modulus");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 31:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=32;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=33;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 32:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Equal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 33:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'=',"Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 34:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=35;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='|'){
state=36;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=37;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 35:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"OR Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 36:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Logical OR");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 37:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'|',"Bitwise OR");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 38:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=39;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='&'){
state=40;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=41;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 39:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"AND Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 40:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Logical AND");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 41:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'&',"Bitwise AND");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 42:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=43;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=44;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 43:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Not Equal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 44:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'!',"Logical NOT");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 45:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=46;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=47;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 46:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"XOR Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 47:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'^',"Bitwise XOR");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 48:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'~',"Bitwise Complement");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 49:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=50;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='>'){
state=51;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=57;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 50:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Greater Than Or Equal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 51:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=52;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='>'){
state=53;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=56;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 52:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Signed Right Shift Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 53:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=54;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=55;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 54:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Unsigned Right Shift Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 55:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Unsigned Right Shift");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 56:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Signed Right Shift");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 57:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'>',"Unsigned Right Shift");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 58:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=59;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else if(lookahead=='<'){
state=60;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=63;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 59:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Less Than Or Equal");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 60:
if(lookahead=='='){
state=61;
lexeme[index++]=lookahead;
lexeme[index]='\0';
charNum=input.read();
break;
}
else{
state=62;
lexeme[index]='\0';
break;
}
case 61:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Signed Left Shift Assign");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 62:
state=0;
currentLexeme="";
for(int i=0;lexeme[i]!='\0';i++){
currentLexeme+= lexeme[i];
}
output.printf("%s %30s %n",currentLexeme,"Signed Left Shift");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 63:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'<',"Less Than");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 64:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'?',"Question Mark");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 65:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",':',"Colon");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 66:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",';',"Semicolon");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 67:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",',',"Comma");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 68:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'.',"Dot");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 69:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'(',"Left Parenthesis");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 70:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",')',"Right Parenthesis");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 71:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'[',"Left Square Bracket");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 72:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",']',"Right Square Bracket");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 73:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'{',"Left Curly Brace");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 74:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'}',"Right Curly Brace");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 75:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\\',"Backslash");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 76:
state=0;
output.printf("%s %30s %n",'\b',"Backspace");
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
case 77: //it is not a recognized character
state=0;
error(output);
index=0; // reset index for other lexemes
break;
}
output.flush();
}
output.close();
input.close();
}
public static void error(PrintWriter out){
out.println("UNRECOGNIZED TOKEN !!!");
}
}
The Heart of the Analyzer
The core of our lexical analyzer is a state machine. Here’s a simplified visualization of how it works:
graph TD
A[Start] --> B{Char Type?}
B -->|Letter| C[Identifier/Keyword]
B -->|Digit| D[Number]
B -->|Symbol| E[Operator/Punctuation]
B -->|Whitespace| F[Ignore]
C --> G{More Chars?}
G -->|Yes| C
G -->|No| H[Emit Token]
D --> I{More Digits?}
I -->|Yes| D
I -->|No| H
E --> H
F --> A
Sample Input and Output
Let’s see our lexical analyzer in action with this input:
//This is sample comment
void main(){
int a,b,c;
a=b+++10;
char x='c';
/* This
is
a
multiline
comment
*/
if (a<b || b==20.5){
string v="Welcome";
}
}
Output (simplified):
| Token | Lexeme |
|---|---|
| KEYWORD | void |
| IDENTIFIER | main |
| LEFT_PARENTHESIS | ( |
| RIGHT_PARENTHESIS | ) |
| LEFT_CURLY_BRACE | { |
| KEYWORD | int |
| IDENTIFIER | a |
| COMMA | , |
| IDENTIFIER | b |
| COMMA | , |
| IDENTIFIER | c |
| SEMICOLON | ; |
| IDENTIFIER | a |
| ASSIGN | = |
| IDENTIFIER | b |
| INCREMENT | ++ |
| PLUS | + |
| INTEGER_LITERAL | 10 |
| SEMICOLON | ; |
| KEYWORD | char |
| IDENTIFIER | x |
| ASSIGN | = |
| CHAR_LITERAL | 'c' |
| SEMICOLON | ; |
| KEYWORD | if |
| LEFT_PARENTHESIS | ( |
| IDENTIFIER | a |
| LESS_THAN | < |
| IDENTIFIER | b |
| LOGICAL_OR | || |
| IDENTIFIER | b |
| EQUAL | == |
| FLOAT_LITERAL | 20.5 |
| RIGHT_PARENTHESIS | ) |
| LEFT_CURLY_BRACE | { |
| KEYWORD | string |
| IDENTIFIER | v |
| ASSIGN | = |
| STRING_LITERAL | "Welcome" |
| SEMICOLON | ; |
| RIGHT_CURLY_BRACE | } |
| RIGHT_CURLY_BRACE | } |
Part 2: The SLR Parser
What is an SLR Parser?
An SLR (Simple LR) Parser is a bottom-up parser for a subset of context-free languages. It’s more powerful than simple precedence parsers but less complex than LALR or Canonical LR parsers.
Our Implementation
Our SLR Parser uses a parsing table to decide its actions. Here’s a simplified view of how it works:
graph TD
A[Start] --> B{Read Input}
B --> C{Check Parsing Table}
C -->|Shift| D[Push to Stack]
C -->|Reduce| E[Apply Production Rule]
C -->|Accept| F[Parsing Complete]
C -->|Error| G[Syntax Error]
D --> B
E --> B
Detailed Implementaion
//class with main method
//importing the necessary packages
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class SLR_Parser{
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{
//hashtable to store the parsing table
Hashtable<String, String> table = new Hashtable<String, String>();
//hashtable to store the productions
Hashtable<String, String> productions = new Hashtable<String, String>();
//inserting the productions into the hashtable
productions.put("E", "E + T");
productions.put("E", "T");
productions.put("T", "T * F");
productions.put("T", "F");
productions.put("F", "( E )");
productions.put("F", "id");
//grammer rules into hashtable to help printing the action
Hashtable<String, String> grammer = new Hashtable<String, String>();
grammer.put("r1", "Reduce by E -> E + T");
grammer.put("r2", "Reduce by E -> T");
grammer.put("r3", "Reduce by T -> T * F");
grammer.put("r4", "Reduce by T -> F");
grammer.put("r5", "Reduce by F -> ( E )");
grammer.put("r6", "Reduce by F -> id");
//shift rules into hashtable to help printing the action
grammer.put("s1", "shift 1");
grammer.put("s2", "shift 2");
grammer.put("s3", "shift 3");
grammer.put("s4", "shift 4");
grammer.put("s5", "shift 5");
grammer.put("s6", "shift 6");
grammer.put("s7", "shift 7");
grammer.put("s8", "shift 8");
grammer.put("s9", "shift 9");
grammer.put("s10", "shift 10");
grammer.put("s11", "shift 11");
grammer.put("accept", "accept");
//inserting the parsing table into the hashtable
table.put("0id", "s5");
table.put("0(", "s4");
table.put("0E", "1");
table.put("0T", "2");
table.put("0F", "3");
table.put("1+", "s6");
table.put("1$", "accept");
table.put("2+", "r2");
table.put("2*", "s7");
table.put("2)", "r2");
table.put("2$", "r2");
table.put("3+", "r4");
table.put("3*", "r4");
table.put("3)", "r4");
table.put("3$", "r4");
table.put("4id", "s5");
table.put("4(", "s4");
table.put("4E", "8");
table.put("4T", "2");
table.put("4F", "3");
table.put("5+", "r6");
table.put("5*", "r6");
table.put("5)", "r6");
table.put("5$", "r6");
table.put("6id", "s5");
table.put("6(", "s4");
table.put("6T", "9");
table.put("6F", "3");
table.put("7id", "s5");
table.put("7(", "s4");
table.put("7F", "10");
table.put("8+", "s6");
table.put("8)", "s11");
table.put("9+", "r1");
table.put("9*", "s7");
table.put("9)", "r1");
table.put("9$", "r1");
table.put("10+", "r3");
table.put("10*", "r3");
table.put("10)", "r3");
table.put("10$", "r3");
table.put("11+", "r5");
table.put("11*", "r5");
table.put("11)", "r5");
table.put("11$", "r5");
//read the input from an input file called input.txt
File file = new File("input.txt");
//scanner to read the input file
Scanner in = new Scanner(file);
while(in.hasNextLine()){
//creating a stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<String>();
//pushing the initial state into the stack
stack.push("0");
//input string
String input = in.nextLine();
//index of the input string
Parser(input, stack, table, productions, grammer);
}
}
//method to parse the input string
public static void Parser(String input, Stack<String> stack,Hashtable<String, String> table, Hashtable<String, String> productions, Hashtable<String, String> grammer){
int index = 0;
//print the stack and current input and action as a table format, each row is separated by a line of dashes
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("Stack\t\t\t\t\t\tInput\t\t\t\tAction");
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
//System.out.printf("%-45s%-35s%-20s\n", stack, input, " ");
//while loop to go through the input string, shift and reduce, considering the parsing table, and consider id as a single token, and $ as the end of the input
while(index < input.length()){
//getting the current state from the stack
String state = stack.peek();
//getting the current input from the input string, it doesn't stop until space
String current = "";
while(index < input.length() && input.charAt(index) != ' '){
current += input.charAt(index);
index++;
}
//getting the action from the parsing table
String action = table.get(state + current);
System.out.printf("%-45s%-35s%-20s\n", stack, current+input.substring(index), grammer.get(action));
//if the action is null, then the input is invalid
if(action == null){
System.out.println("Syntax Error");
break;
}
//if the action is accept, then the input is valid
else if(action.equals("accept")){
break;
}
//if the action is shift, then push the current input and the next state into the stack
else if(action.charAt(0) == 's'){
stack.push(current);
stack.push(action.substring(1));
index++;
}
//if the action is reduce, then pop the stack as twice as the length of the white spaces in production rule, then push the non-terminal and the next state into the stack
else if(action.charAt(0) == 'r'){
int length = 0;
char nonTerminal = ' ';
//if the production rule is E->T, then the length is 1
if(action.charAt(1) == '2'){
length = 1;
nonTerminal = 'E';
}
//if the production rule is E->E+T, then the length is 3
else if(action.charAt(1) == '1'){
length = 3;
nonTerminal = 'E';
}
//if the production rule is T->F, then the length is 1
else if(action.charAt(1) == '4'){
length = 1;
nonTerminal = 'T';
}
//if the production rule is T->T*F, then the length is 3
else if(action.charAt(1) == '3'){
length = 3;
nonTerminal = 'T';
}
//if the production rule is F->id, then the length is 1
else if(action.charAt(1) == '6'){
length = 1;
nonTerminal = 'F';
}
//if the production rule is F->(E), then the length is 3
else if(action.charAt(1) == '5'){
length = 3;
nonTerminal = 'F';
}
//pop the stack as twice as the length of the white spaces in production rule
for(int i = 0; i < length * 2; i++){
stack.pop();
}
//push the non-terminal and the next state into the stack
String nextState = stack.peek()+nonTerminal;
//print nextState
stack.push(nonTerminal + "");
stack.push(table.get(nextState));
index--;
}
}
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------");
}
}
The Parsing Table
The heart of our SLR Parser is its parsing table. Here’s a glimpse of how it’s structured:
table.put("0id", "s5");
table.put("0(", "s4");
table.put("0E", "1");
table.put("0T", "2");
table.put("0F", "3");
// ... more entries ...
Sample Input and Output
Let’s see our SLR Parser in action with these inputs:
id * ( id + id ) $( id + id ) * id $
For the input:
id * ( id + id ) $
| Stack | Input | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | id*(id+id)$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 id 5 | *(id+id)$ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 F 3 | *(id+id)$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 T 2 | *(id+id)$ | Shift 7 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 | (id+id)$ | Shift 4 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 | id+id)$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 id 5 | +id)$ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 F 3 | +id)$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 T 2 | +id)$ | Shift 6 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 T 2 + 6 | id)$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 T 2 + 6 id 5 | )$ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 T 2 + 6 F 3 | )$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 T 2 + 6 T 9 | )$ | Reduce by E -> T + T |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 E 8 | )$ | Shift 11 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 ( 4 E 8 ) 11 | $ | Reduce by F -> ( E ) |
| 0 T 2 * 7 F 10 | $ | Reduce by T -> T * F |
| 0 T 2 | $ | Reduce by E -> T |
| 0 E 1 | $ | Accept |
For the input:
( id + id ) * id $
| Stack | Input | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | (id+id)*id$ | Shift 4 |
| 0 ( 4 | id+id)*id$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 ( 4 id 5 | +id)*id$ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 ( 4 F 3 | +id)*id$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 ( 4 T 2 | +id)*id$ | Shift 6 |
| 0 ( 4 T 2 + 6 | id)*id$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 ( 4 T 2 + 6 id 5 | )*id$ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 ( 4 T 2 + 6 F 3 | )*id$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 ( 4 T 2 + 6 T 9 | )*id$ | Reduce by E -> T + T |
| 0 ( 4 E 8 | )*id$ | Shift 11 |
| 0 ( 4 E 8 ) 11 | *id$ | Reduce by F -> ( E ) |
| 0 F 3 | *id$ | Reduce by T -> F |
| 0 T 2 | *id$ | Shift 7 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 | id$ | Shift 5 |
| 0 T 2 * 7 id 5 | $ | Reduce by F -> id |
| 0 T 2 * 7 F 10 | $ | Reduce by T -> T * F |
| 0 T 2 | $ | Reduce by E -> T |
| 0 E 1 | $ | Accept |
Conclusion
Building a lexical analyzer and SLR parser from scratch provides deep insights into how compilers work. This project demonstrates the power of Java in implementing complex language processing tools.
Future Enhancements
- Extend the lexical analyzer to support more complex tokens
- Implement error recovery in the SLR parser
- Develop a semantic analyzer as the next step in building a complete compiler
Remember, in the world of compiler design, we’re not just writing code; we’re creating the tools that understand code!